Read Also
Navigating Compliance Challenges in ESG AML and Digital Onboarding
Chuan Lim Ang, Managing Director and SG Head of Compliance, CIMB
A Vision for the Future: Automation, Robotics, and the Smart Factory
Joe Tilli, State Industrial Automation Sales Manager, Lawrence & Hanson
The Rise of Hyper Automation
Erdenezaya Batnasan, Head of IT End-User Support Service Department, Khan Bank
Transforming Business Operations with Robotic Process Automation
Simon So, CMGR, MCMI, Regional Head of Digital Solutions, Richemont Asia Pacifi
Combining Automation with AI to Achieve Human-Like Interaction
Kain Chow, General Manager, Technology & Transformation, New World Development Company Limited
Implementing RPA - 5 Ultimate Prerequisite
Indra Hidayatullah, Data Management & Analytics Division Head, Pt. Bank Tabungan Negara
Incorporating the power of recognition into our vendors' sustainability journey
Cynthia Khoo, Head, Central Procurement Office, OCBC Bank (Malaysia) Berhad
Elevating Guest Experience with Data
Clive Edwards, Senior Vice President, Operations, Capella Hotel Group













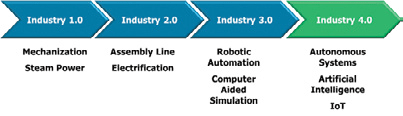 The mega trends are also increasing the volume of data acquisition, processing, and analytics. Implementation of sensors in the industrial manufacturing has also grown significantly in alignment with advancement in sensor technologies. Key sensing strategies to enable wide industry adoption include scalable sensor product platforms and plug-and-play interfaces. By leveraging on top-down product platform development, sensor manufacturers can provide product derivatives and multiple product form factors very cost effectively by leveraging on core sensing components and devices. By incorporating plug-and-play interfaces into the product platform development strategy, sensor manufacturers are also able to provide seamless implementation and network connectivity.
The mega trends are also increasing the volume of data acquisition, processing, and analytics. Implementation of sensors in the industrial manufacturing has also grown significantly in alignment with advancement in sensor technologies. Key sensing strategies to enable wide industry adoption include scalable sensor product platforms and plug-and-play interfaces. By leveraging on top-down product platform development, sensor manufacturers can provide product derivatives and multiple product form factors very cost effectively by leveraging on core sensing components and devices. By incorporating plug-and-play interfaces into the product platform development strategy, sensor manufacturers are also able to provide seamless implementation and network connectivity.
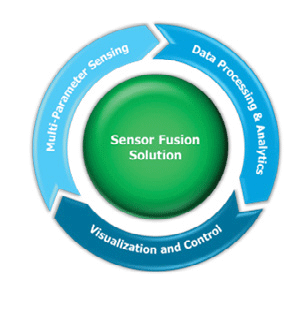
 Multi-parameter sensing comprises of high-precision measurement with data integrity. Data processing and analytics provide critical interpretation of multiple parameter measurements. Visualization and control enable efficient and effective task management of manufacturing processes.
Multi-parameter sensing comprises of high-precision measurement with data integrity. Data processing and analytics provide critical interpretation of multiple parameter measurements. Visualization and control enable efficient and effective task management of manufacturing processes.
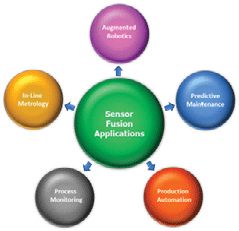
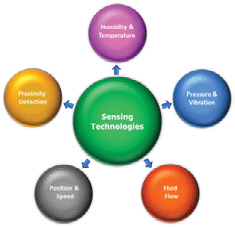 Key intelligent sensing technologies for environmental monitoring, physical parameter measurement, and motion control are illustrated in Fig. 3 and key examples of innovative sensor fusion applications are illustrated in Fig. 4. Multiple sensing technologies are implemented in each key application. Augmented robotics, for example, requires intuitive human-machine interaction and control interfaces. Tactile pressure sensing enhances dexterity manipulation whilst proximity detection provides a critical safety function to prevent injury or damage.
The future of manufacturing will accelerate the implementation of cyber physical systems, cybersecurity, and connected enterprise network. Advancement of sensor fusion technology platforms and solutions will enable the innovation continuum across devices, systems and applications in Industry 4.0 and beyond.
Key intelligent sensing technologies for environmental monitoring, physical parameter measurement, and motion control are illustrated in Fig. 3 and key examples of innovative sensor fusion applications are illustrated in Fig. 4. Multiple sensing technologies are implemented in each key application. Augmented robotics, for example, requires intuitive human-machine interaction and control interfaces. Tactile pressure sensing enhances dexterity manipulation whilst proximity detection provides a critical safety function to prevent injury or damage.
The future of manufacturing will accelerate the implementation of cyber physical systems, cybersecurity, and connected enterprise network. Advancement of sensor fusion technology platforms and solutions will enable the innovation continuum across devices, systems and applications in Industry 4.0 and beyond.









